How BMS-986489 Works in SCLC
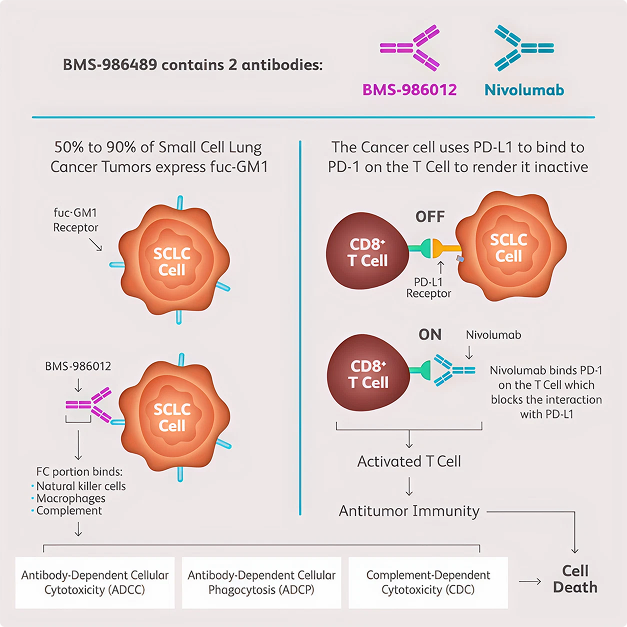
- Fucosyl GM1 (Fuc-GM1) is a glycosphingolipid expressed predominately on lung cancers and limited on normal tissue. Tumor expression estimates: 50-90% of SCLC. Normal tissue expression limited to peripheral nerve.
- BMS-986012 (atigotatug) is a non-fucosylated human IgG1 antibody that binds selectively to Fuc-GM1.
- Pre-clinically, binding of atigotatug to tumor cells results in tumor cell death via: antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC); antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP); complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC).
Both atigotatug and nivolumab can individually lead to tumor cell death, through distinct but complementary mechanisms of action.
Reference: Ponath P et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Oct 15; 24(20):5178-89